
Get back into balance with Potassium
Potassium is the most important dietary electrolyte. We require huge amounts compared to other nutrients. Potassium is necessary for a regular heartbeat and the maintenance of normal blood pressure. It helps regulate the electrolyte balance in our cells, maintain an optimal acidity (pH), and deliver blood glucose into our cells to convert to energy.
We source most of our potassium requirements from our diet. The body is able to absorb potassium from a wide range of foods, especially fruit and vegetables, carbohydrates, and even drinks such as milk, tea and coffee. Almost all of the body’s potassium, up to 98%, is held inside our cells. It works with other electrolytes such as sodium, calcium and magnesium to maintain our electrolyte balance and absorb minerals from the food we eat.
✔️ Regulates normal blood pressure
✔️ Maintains fluid balance in our cells
✔️ Maintain the correct acidity (pH) of our blood and cells.
✔️ Helps convert blood glucose to energy
✔️ Helps the body absorb minerals from food
Sodium and Potassium for balance
The relationship of sodium to potassium is important for your overall health. A low-sodium diet enhances potassium conservation, whereas a high-sodium diet promotes potassium excretion. Studies have shown a connection between high potassium intake and healthier blood pressure. This in turn can help prevent cardiac arrest or the chance of a stroke.
Potassium works with sodium to regulate the flow of nutrients in and out of the trillions of cells in the body. If this flow is thrown out of balance, cells can quickly die and blood pressure is affected and our heart can not function correctly. Numerous studies have shown that a low potassium/high sodium diet plays a role in the development of cancer and cardiovascular disease.
The Recommended Dietary Intakes (RDI) in the USA is much higher than in New Zealand. According to current guidelines, American adults require 4,700mg of potassium, and 1,200mg of sodium daily, or a ratio of nearly four-to-one. However, studies indicate that the average American intake is almost one-to-one, due to excess salt in the diet.
It is estimated that a third of our body and brain energy is used in maintaining the balance of potassium and sodium, controlling water balance and distribution, muscle and nerve cell function, pH balance, and kidney and adrenal function.

Magnesium and Potassium for energy
These two important electrolytes are important for energy production, and if you are lacking both potassium and magnesium, you may suffer from low energy levels, and in some cases chronic fatigue syndrome.
When suffering from low energy or fatigue, supplementing with both potassium and magnesium can replace lost minerals, achieve optimal balance throughout the body and restore energy levels, often within a few days.
Signs of Potassium deficiency
Some of the warning signs of a potassium deficiency include fatigue, mental confusion, irritability, weakness, headaches, muscle cramps, problems in nerve conduction and muscle contraction and heart disturbances. People with Type 2 diabetes are often low in the mineral.
Potassium is mostly lost through urination. As the body flushes out excess sodium, a large amount potassium goes with it, as the sodium quickly links with potassium during digestion.
It can also be lost through excessive sweating or vigorous exercise, so it’s helpful to replace and replenish by eating raw fruit or an electrolyte drink during or after a workout.
Excessive fluid loss, and the use of diuretics and laxatives are the most common causes of deficiency. As fluid retention can be a symptom of low potassium status, it may help to supplement with potassium instead of opting for diuretic drugs, but you should of course consult your health professional first before undergoing supplementation.
Sugary drinks and alcohol can also deplete potassium stores.
Low-carb diets are becoming increasing popular, and if you’re struggling for energy or losing muscle, it may be due to a lack of potassium, which is commonly sourced from carbohydrate-rich fruit and vegetables, as well as other carbohydrates such as bread.
A diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables and low in sodium should help maintain optimal potassium levels.In a study of vegetarians and non-vegetarians, significantly lower blood pressure was found in vegetarians across every age group. Only 2% of the vegetarians had hypertension, compared to 26% hypertension in the non-vegetarian group. While other factors may be at play, this study shows that obtaining good levels of potassium from a diet rich in fruit and vegetables can play an important role in the regulation of blood pressure and may protect against the development of cardiovascular disease.
Food sources of Potassium
Potassium is found in the cells of a wide variety of plant and and animal foods; meat, milk, fruits, vegetables, grains and legumes.
Leafy green vegetables and fruits that grow on vines such as tomatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, eggplant and pumpkin are the best sources.
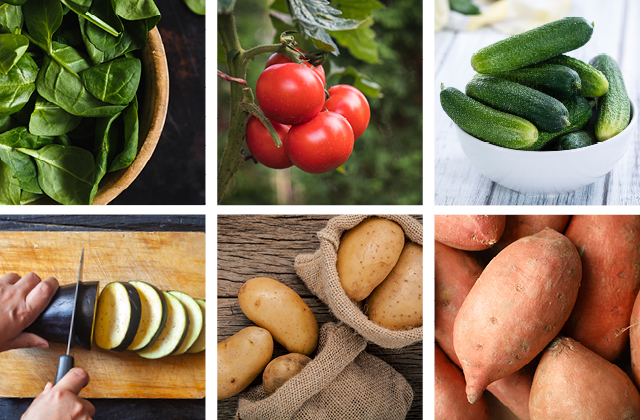

Root vegetables such as potatoes, kūmara and taro contribute the most potassium in our diets according to the latest New Zealand Nutritional Survey. Milk, coffee, tea and other non-alcoholic drinks also provide good sources in the New Zealand diet.
When boiling vegetables, you can lose up to 50% of the potassium, but this can be retained if the cooking water is consumed.
Aren’t bananas a good source of Potassium?
As brazil nuts are associated with Selenium, bananas are often the first foods to come to mind when thinking about potassium. However, it’s estimated that only 40% of the potassium in a banana is absorbed, due to the lack of chloride in the fruit. This lack of absorption is often not allowed for when estimating mineral intake in food tables. This can explain why potassium chloride is often recommended when looking to supplement, as it helps with absorption.

Supplementing with Potassium
Recommended Dietary Intakes (RDI) in New Zealand are lower than other countries, and range from 2,500mg for young females, to 3,800mg for adult males. As the permitted level of potassium allowed in supplements is only 100mg, it’s important to access as much from your diet as possible by eating plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables and moderating your salt intake.
Many salt substitutes contain potassium chloride as a replacement for the sodium chloride in salt. The potassium content can vary widely, so for those on medication or with kidney disease it’s best to talk with your health care professional before taking salt substitutes because of the risk of hypokalaemia.
When supplementing, do not exceed recommended dosage and keep potassium supplements out of reach of children. People with heart, adrenal gland, kidney disease or should consult with a health care professional before use. Potassium may interfere with some prescription and non-prescription medications such as diuretics so seek advice on what’s best to take and when.

Summary
As a rule, all of us generally need a lot more potassium in our diets and a lot less sodium. The simplest way of achieving this is eating plenty of fresh fruits and leafy green vegetables and avoiding salty snacks, fast foods, and ready-made cakes and biscuits and other heavily processed options, which contain significant amounts of sodium.
-
 Potassium Liquid Mineral$27.90
Potassium Liquid Mineral$27.90 -
 Magnesium Liquid Mineral$27.90
Magnesium Liquid Mineral$27.90
Disclaimer:
The information in this article is not intended as a medical prescription for any disease or illness. Nothing stated here should be considered medical advice. Use as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your healthcare professional.
Coory, D. Stay Healthy by supplying what’s lacking in your diet. 1992
Schauss, Alexander G. Minerals, Trace Elements, & Human Health. Life Sciences Press. 1995
Nutrition’s dynamic duos. Harvard Health Publishing. 2009
National Institutes of Health (NIH) Potassium. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Updated 2021
Ministry of Health, A Focus on Nutrition: Key Findings of the 2008/09 New Zealand Adult Nutrition Survey, 2011.

